In image processing, optics is one of the most important elements that directly affects the quality, accuracy and analysis efficiency of the images obtained. Factors such as correct lens selection, focal length, aperture and optical distortions play a critical role in many areas from industrial applications to machine vision. In this article, we comprehensively review the optical components used in image processing systems.
What is Lens?
Görüntüleme sistemlerinin en temel bileşenlerinden biri olan lens (mercek), ışık ışınlarının yönünü değiştirerek odaklanmasını sağlar. Genellikle camdan üretilen bu optik araçlar, ışığı kırarak algılayıcıya net bir görüntü iletilmesini mümkün kılar.
Net Area (Floor Area)
Lenses produce a circular image, the sharpest part of which is the center. The diameter of the sharpest area within this circle is called the “footprint.” However, image sensors are usually rectangular, so the results are also rectangular.
Odak Uzaklığı ve Lens Türleri
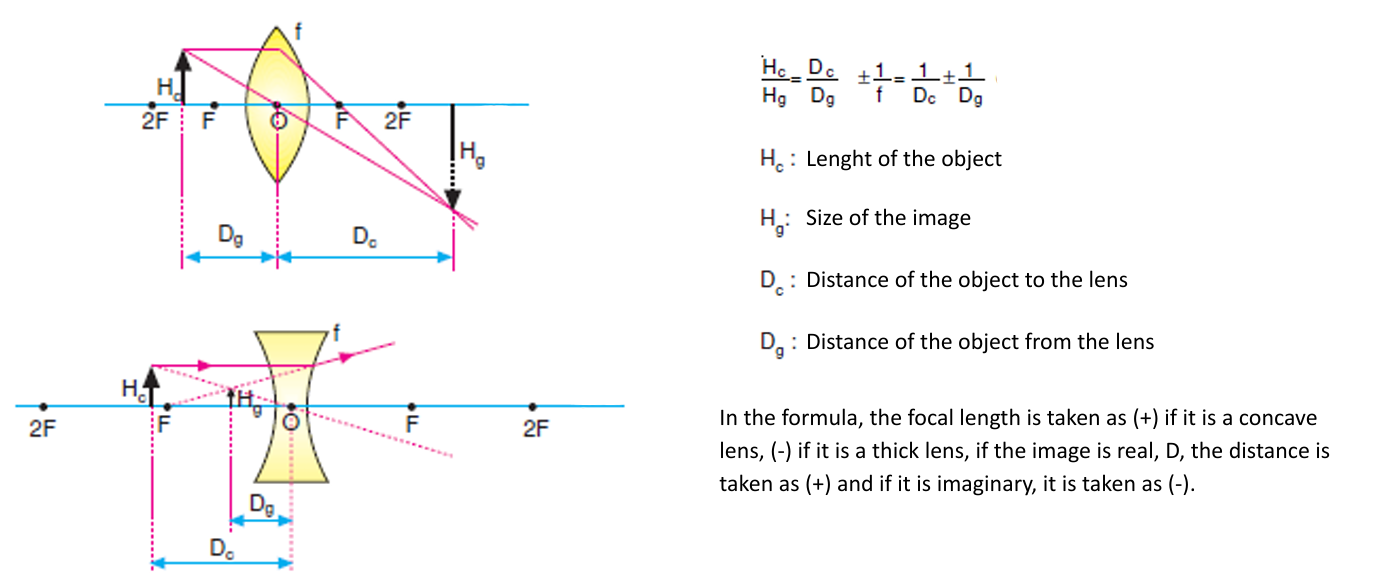
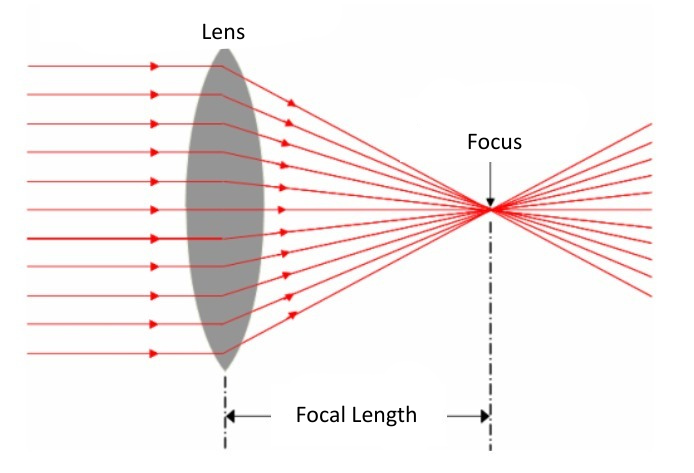
The distance between the final lens and the image sensor is called the “focal length” and is measured in millimeters. According to focal length, lenses are classified as follows:
-
Fisheye Lenses: 6-10mm, 180° angle of view
-
Ultra Wide Angle: 10-24mm
-
Wide Angle: 24-40mm
-
Standard: 40-50mm
-
Tele Lens: 50mm üzeri
-
Super Tele: 200mm üzeri
How to Adjust Manual Focus?
Manual focus adjustment should be made to obtain optimum clarity in the image. In this process, the focus ring, aperture and light control should be evaluated together. In order to measure the depth of field and to achieve correct focus, the aperture is brought to maximum aperture to provide clarity, then the light intensity and shutter speed are brought into balance.
Lens Format and Image Circle Diameters
The words 1/2″, 2/3″ on lenses indicate the image circle diameters. For example, a 1/2″ lens can be used with a 1/3″ sensor, but vignetting may occur at the edges of the image.

The Effect of Aperture on the Image
Aperture directly affects the brightness and depth of field of an image. Wide apertures (low f-numbers) create shallow depth of field, while narrow apertures (high f-numbers) allow larger areas to be in focus.
Types of Optical Distortion
Various optical distortions can occur due to the structural features of lenses:
- Barrel distortion
- Pincushion distortion
- Handlebar moustache distortion
- Rolling shutter distortion
- Moire distortion

Barrel distortion, in particular, manifests itself as straight lines bending outward from the image center toward the edges. This distortion becomes more pronounced with lenses with short focal lengths.
Examples of Deterioration
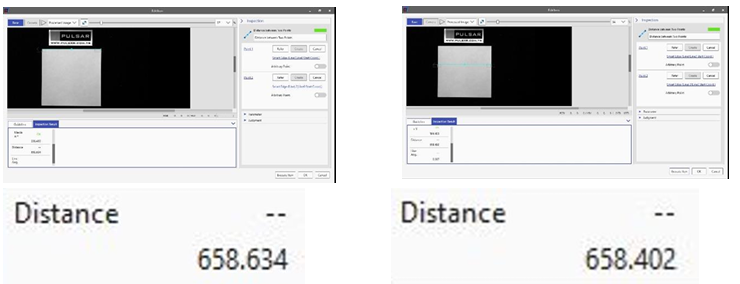
Measured with a 6.5mm focal length lens, the difference between the top and bottom widths on the paper is approximately 2.268mm. This difference is the effect of barrel distortion.
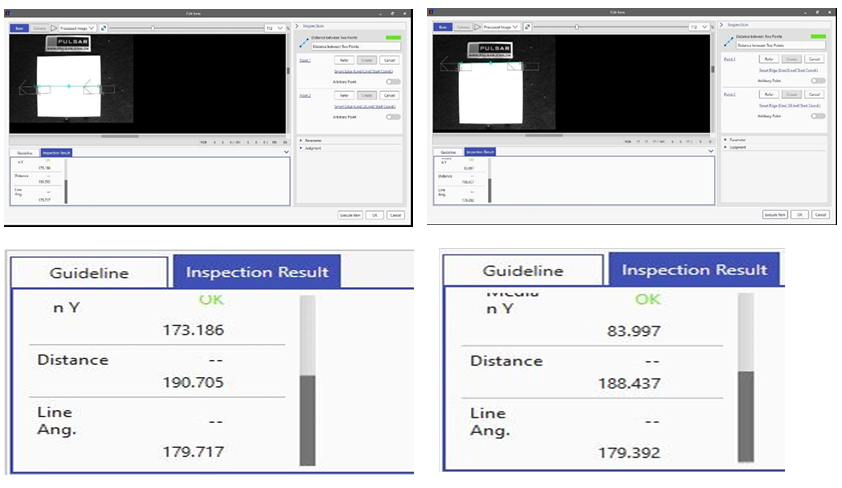
When the same experiment was repeated with a 75mm focal length lens, the difference was only 0.232mm, indicating that longer focal length lenses provide more accurate measurements.
Choosing the right optics in image processing directly affects the accuracy of the data obtained and the quality of analysis. Choosing the most suitable lens for the application is critical, considering factors such as the focal length of the lens, aperture and optical distortion rates. You can contact our experts for the right optics selection in image processing.

